What Does ASMR Stand For? (+Benefits)
The acronym describes a sensory phenomenon characterized by a tingling sensation that typically begins on the scalp and spreads down the neck and upper spine. This experience is often triggered by specific auditory or visual stimuli, such as whispering, tapping, or slow hand movements. It is frequently associated with feelings of relaxation, calmness, and well-being.
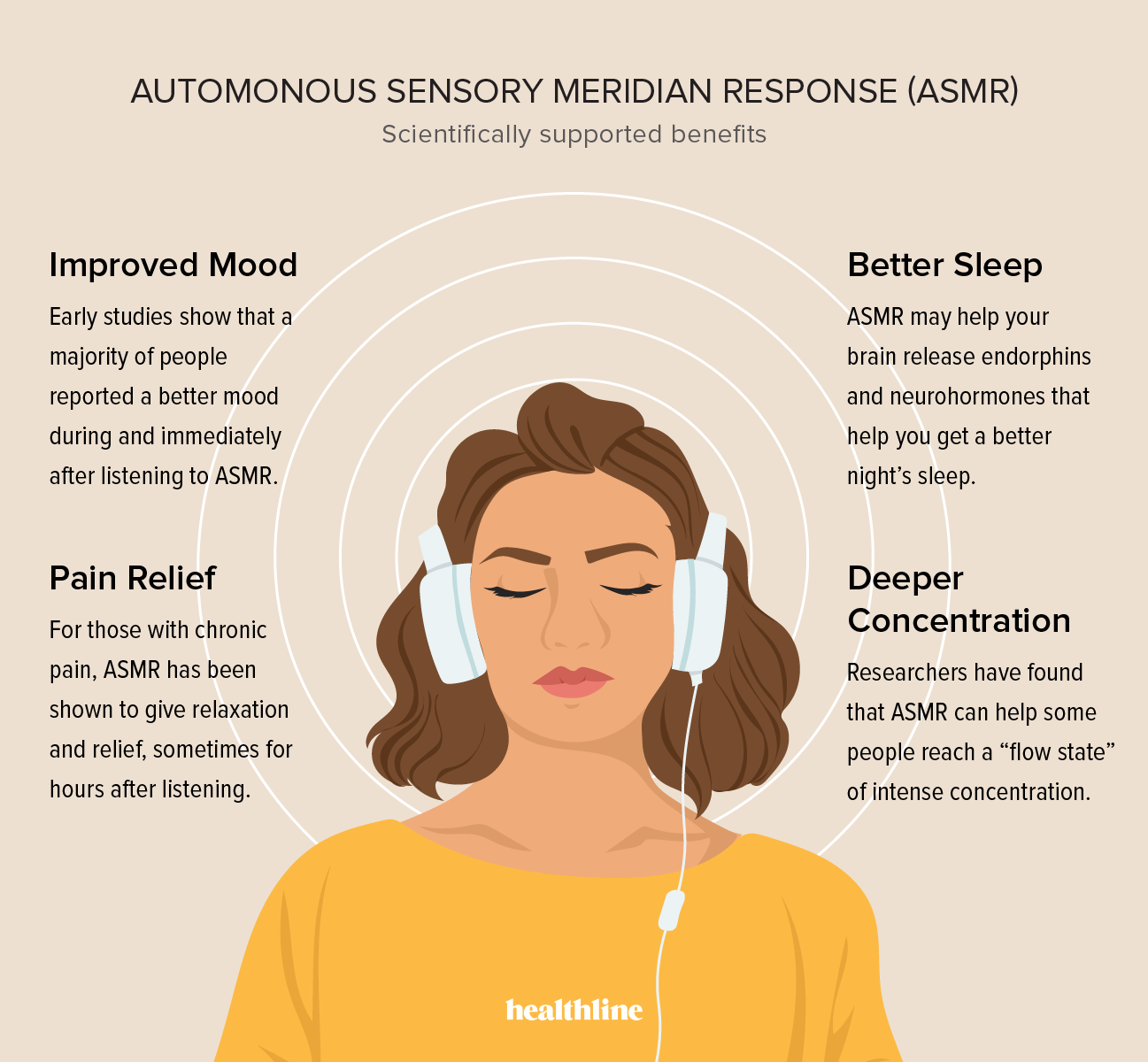
The sensation's increasing recognition is due to its potential therapeutic applications in stress reduction and sleep improvement. While research is ongoing, anecdotal evidence suggests that individuals may utilize recorded or live triggering content to manage anxiety or insomnia. The origins of the term itself are relatively recent, gaining traction online as communities formed around shared experiences.
The following sections will delve into the science behind these sensations, explore common triggers, and discuss the potential benefits and criticisms associated with the phenomenon, offering a more comprehensive understanding.
- Mzansi Man Documents Sa Potholes Viral Tiktok
- Tammy Camacho Obituary A Remarkable Life Remembered
- Does Robert Ri Chard Have A Wife
- Najiba Faiz Video Leaked On Telegram New
- Did Tori Bowie Baby Survive What Happened
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the meaning and understanding of the acronym.
Question 1: Is the sensation a universal experience?
No, it is not. While many individuals report experiencing the tingling sensation, others do not. The ability to experience it appears to vary between individuals.
- Kathy Griffin S Husband Was An Unflinching
- Meet Ezer Billie White The Daughter Of
- Beloved Irish Father Clinton Mccormack Dies After
- Janice Huff And Husband Warren Dowdy Had
- Bad Bunny Used To Make Mix Cds
Question 2: Is the experience sexually arousing?
While some individuals may experience a mild sense of arousal, it is generally considered distinct from sexual arousal. The primary sensation is one of relaxation and well-being, not sexual excitement.
Question 3: Is it scientifically proven?
Research is ongoing, but definitive scientific proof is still emerging. Studies have used brain imaging techniques to observe physiological changes associated with the experience, but more research is needed to fully understand the underlying mechanisms.
Question 4: Are there any negative side effects?
For most individuals, there are no significant negative side effects. However, some individuals may find certain triggers irritating or unpleasant. It is important to be mindful of one's own sensitivities.
Question 5: Can anyone learn to experience the sensation?
It is unlikely that someone who does not naturally experience the sensation can learn to do so. Responsiveness appears to be an innate characteristic.
Question 6: Is it a form of synesthesia?
While there are some similarities to synesthesia, it is generally considered a distinct phenomenon. Synesthesia involves the blending of different senses, while it primarily involves a specific tingling sensation in response to specific triggers.
In summary, it refers to a unique sensory experience that varies among individuals and is still under scientific investigation. Its potential applications in stress reduction and relaxation warrant further exploration.
The following section will explore the variety of stimuli recognized as triggers for this phenomenon.
Tips
The following provides guidance for comprehending the nuances of this sensory experience. These tips aim to clarify its nature and potential applications.
Tip 1: Differentiate from Sexual Arousal: It is important to recognize that, while some individuals may experience a mild sense of arousal, it is fundamentally distinct from sexual excitement. The core sensation is relaxation, not sexual stimulation.
Tip 2: Approach Scientific Claims with Caution: While research is ongoing, definitive scientific conclusions regarding its mechanisms are still developing. Critically evaluate claims and rely on peer-reviewed studies rather than anecdotal evidence.
Tip 3: Consider Individual Variability: The experience is highly subjective. Triggers and responses vary significantly from person to person. Avoid generalizations and focus on understanding individual experiences.
Tip 4: Be Mindful of Terminology: Use precise language when discussing the sensation. Avoid casual or dismissive terms that may trivialize the experience for those who find it beneficial.
Tip 5: Explore Trigger Categories Systematically: If attempting to identify personal triggers, explore common categories such as auditory (whispering, tapping), visual (slow hand movements), and tactile (light touch) stimuli in a structured manner.
Tip 6: Recognize Potential Therapeutic Applications: While not a substitute for professional medical care, it may offer potential benefits in managing stress, anxiety, and insomnia. Explore its applications responsibly and in consultation with healthcare professionals.
Tip 7: Acknowledge the Lack of Universal Experience: Understand that not everyone experiences the sensation. Avoid pressuring or questioning those who do not report experiencing it.
By understanding its nuances, individual variability, and the limitations of current scientific knowledge, a more informed perspective can be cultivated. This comprehension is crucial for discussions surrounding its nature and application.
The following sections will summarize the key points and provide a conclusion to this exploration.
Conclusion
This exploration clarified the meaning of the acronym, designating a sensory phenomenon characterized by a tingling sensation often triggered by auditory or visual stimuli. Its increasing recognition is attributed to potential applications in stress reduction and sleep improvement, despite ongoing research into its underlying mechanisms. Distinguishing it from sexual arousal and acknowledging individual variability in experiencing the sensation were emphasized.
Further investigation is warranted to fully understand the physiological and psychological underpinnings of what does asmr stand for. Continued research will determine its efficacy as a therapeutic tool and provide a more comprehensive understanding of this unique sensory experience, potentially expanding its responsible and beneficial applications.
- Layke Leischner Car Accident Resident Of Laurel
- Beloved Irish Father Clinton Mccormack Dies After
- Is Max Muncy Christian Or Jewish Religion
- Does Robert Ri Chard Have A Wife
- Hilaree Nelson Wiki Missing Husband Family Net

ASMR Meaning What Does "ASMR" Stand For? • 7ESL Autonomous sensory
Autonomous Sensory Meridian Response (ASMR) Science & History

WHAT DOES ASMR STAND FOR? YouTube